How To Add A New Forest In Windows Server 2016
This browser is no longer supported.
Upgrade to Microsoft Edge to take reward of the latest features, security updates, and technical support.
Install a New Windows Server 2012 Active Directory Woods (Level 200)
Applies to: Windows Server 2022, Windows Server 2019, Windows Server 2016, Windows Server 2012 R2, Windows Server 2012
This topic explains the new Windows Server 2012 Active Directory Domain Services domain controller promotion feature at an introductory level. In Windows Server 2012, Advertizement DS replaces the Dcpromo tool with a Server Director and Windows PowerShell-based deployment arrangement.
-
Active Directory Domain Services Simplified Assistants
-
Technical Overview
-
Deploying a Forest with Server Manager
-
Deploying a Woods with Windows PowerShell
Active Directory Domain Services Simplified Administration
Windows Server 2012 introduces the next generation of Active Directory Domain Services Simplified Administration, and is the most radical domain re-envisioning since Windows 2000 Server. Advertising DS Simplified Administration takes lessons learned from twelve years of Active Directory and makes a more supportable, more flexible, more intuitive administrative experience for architects and administrators. This meant creating new versions of existing technologies equally well as extending the capabilities of components released in Windows Server 2008 R2.
What Is AD DS Simplified Administration?
AD DS Simplified Administration is a reimagining of domain deployment. Some of those features include:
-
AD DS function deployment is at present role of the new Server Managing director compages and allows remote installation.
-
The AD DS deployment and configuration engine is now Windows PowerShell, even when using a graphical setup.
-
Promotion at present includes prerequisite checking that validates forest and domain readiness for the new domain controller, lowering the chance of failed promotions.
-
The Windows Server 2012 forest functional level does not implement new features and domain functional level is required but for a subset of new Kerberos features, relieving administrators of the frequent need for a homogenous domain controller environment.
Purpose and Benefits
These changes may appear more circuitous, non simpler. In redesigning the AD DS deployment process though, there was opportunity to coalesce many steps and best practices into fewer, easier actions. This means, for example, that the graphical configuration of a new replica domain controller is now eight dialogs rather than the previous twelve. Creating a new Agile Directory forest requires a single Windows PowerShell control with just one argument: the name of the domain.
Why is in that location such an emphasis on Windows PowerShell in Windows Server 2012? As distributed computing evolves, Windows PowerShell allows a unmarried engine for configuration and maintenance from both graphical and command-line interfaces. It permits fully featured scripting of any component with the same first form citizenship for an Information technology Professional that an API grants to developers. Equally cloud-based computing becomes ubiquitous, Windows PowerShell besides finally brings the power to remotely administer a server, where a computer with no graphical interface has the same management capabilities as one with a monitor and mouse.
A veteran Ad DS administrator should detect their previous knowledge highly relevant. A kickoff administrator will find a far shallower learning curve.
Technical Overview
What You Should Know Before You Begin
This topic assumes familiarity with previous releases of Active Directory Domain Services, and does non provide foundational detail effectually their purpose and functionality. For more information about AD DS, meet the TechNet Portal pages linked below:
-
Active Directory Domain Services for Windows Server 2008 R2
-
Active Directory Domain Services for Windows Server 2008
-
Windows Server Technical Reference
Functional Descriptions
Advert DS Role Installation
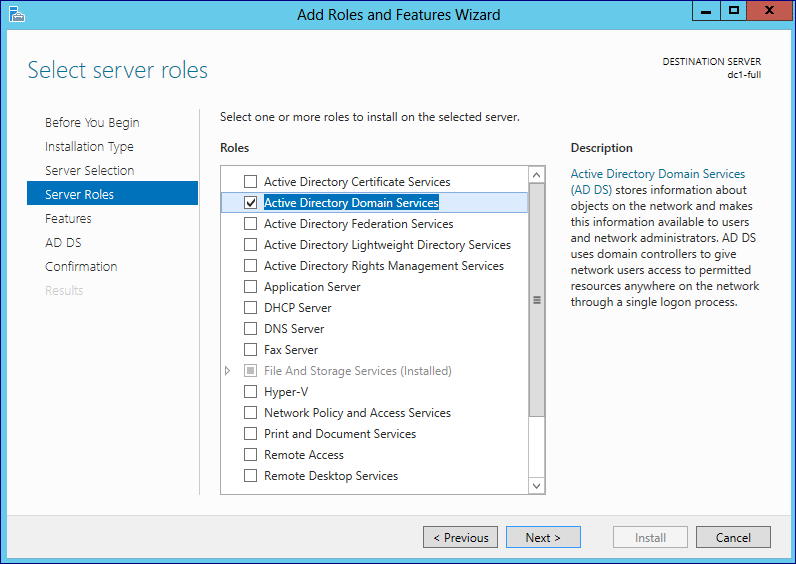
Active Directory Domain Services installation uses Server Manager and Windows PowerShell, like all other server roles and features in Windows Server 2012. The Dcpromo.exe plan no longer provides GUI configuration options.
You apply a graphical wizard in Server Managing director or the ServerManager module for Windows PowerShell in both local and remote installations. By running multiple instances of those wizards or cmdlets and targeting unlike servers, yous can deploy AD DS to multiple domain controllers simultaneously, all from one unmarried panel. Although these new features are not backwards compatible with Windows Server 2008 R2 or earlier operating systems, you tin also still use the Dism.exe application introduced in Windows Server 2008 R2 for local role installation from the archetype control-line.
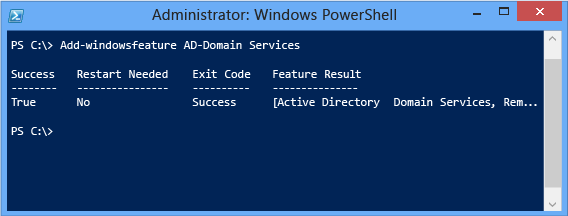
Advertisement DS Role Configuration
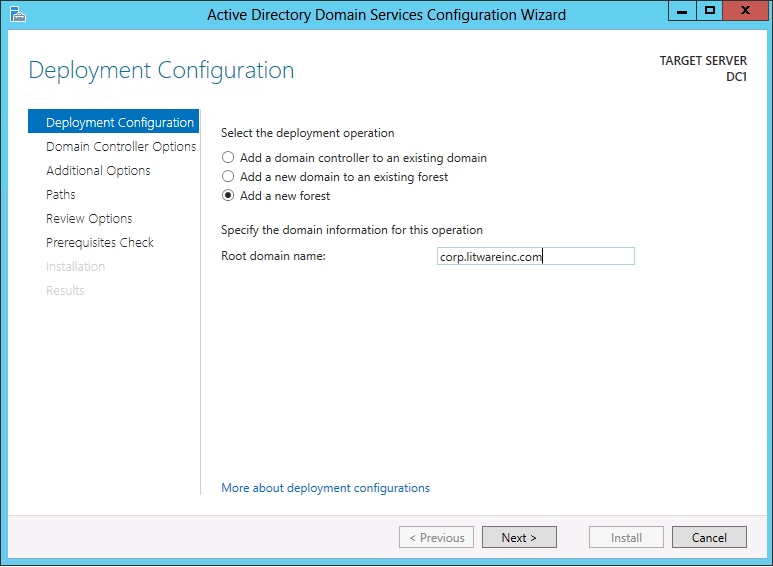
Active Directory Domain Services configuration " previously known as DCPROMO " is a now a discrete operation from role installation. After installing the AD DS role, an administrator configures the server as a domain controller using a carve up wizard within Server Managing director or using the ADDSDeployment Windows PowerShell module.
Advertizement DS part configuration builds on twelve years of field experience and now configures domain controllers based on the near recent Microsoft all-time practices. For example, Domain Name System and Global Catalogs install by default on every domain controller.
The Server Manager Ad DS configuration sorcerer merges many individual dialogs into fewer prompts and no longer hides settings in an "advanced" mode. The entire promotion process is in 1 expanding dialog box during installation. The sorcerer and the ADDSDeployment Windows PowerShell module show you lot notable changes and security concerns, with links to farther information.
The Dcpromo.exe remains in Windows Server 2012 for command-line unattended installations only, and no longer runs the graphical installation wizard. Information technology is highly recommended that you discontinue utilize of Dcpromo.exe for unattended installs and replace information technology with the ADDSDeployment module, as the now-deprecated executable will not be included in the adjacent version of Windows.
These new features are not backwards compatible to Windows Server 2008 R2 or older operating systems.
Of import
Dcpromo.exe no longer contains a graphical wizard and no longer installs role or feature binaries. Attempting to run Dcpromo.exe from the Explorer shell returns:
"The Active Directory Domain Services Installation Magician is relocated in Server Managing director. For more information, run into https://go.microsoft.com/fwlink/?LinkId=220921."
Attempting to run Dcpromo.exe /unattend even so installs the binaries, as in previous operating systems, only warns:
"The dcpromo unattended operation is replaced by the ADDSDeployment module for Windows PowerShell. For more information, see https://go.microsoft.com/fwlink/?LinkId=220924."
Windows Server 2012 deprecates dcpromo.exe and it will non be included with future versions of Windows, nor will it receive further enhancements in this operating organisation. Administrators should discontinue its employ and switch to the supported Windows PowerShell modules if they wish to create domain controllers from the control-line.
Prerequisite Checking
Domain controller configuration also implements a prerequisite checking phase that evaluates the forest and domain prior to continuing with domain controller promotion. This includes FSMO role availability, user privileges, extended schema compatibility and other requirements. This new design alleviates issues where domain controller promotion starts and then halts midway with a fatal configuration fault. This lessens the chance of orphaned domain controller metadata in the forest or a server that incorrectly believes information technology is a domain controller.
Deploying a Forest with Server Manager
This department explains how to install the starting time domain controller in a woods root domain using Server Director on a graphical Windows Server 2012 computer.
Server Manager Advertizing DS Office Installation Procedure
The diagram below illustrates the Active Directory Domain Services office installation procedure, beginning with you lot running ServerManager.exe and ending right before the promotion of the domain controller.
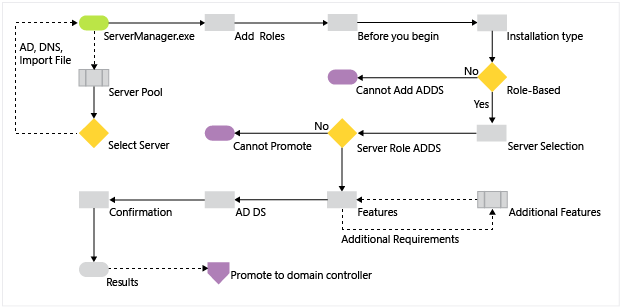
Server Pool and Add together Roles
Any Windows Server 2012 computers attainable from the computer running Server Director are eligible for pooling. Once pooled, you select those servers for remote installation of Ad DS or any other configuration options possible inside Server Manager.
To add together servers, choose i of the following:
-
Click Add Other Servers to Manage on the dashboard welcome tile
-
Click the Manage carte du jour and select Add Servers
-
Correct-click All Servers and choose Add Servers
This brings upwards the Add together Servers dialog:
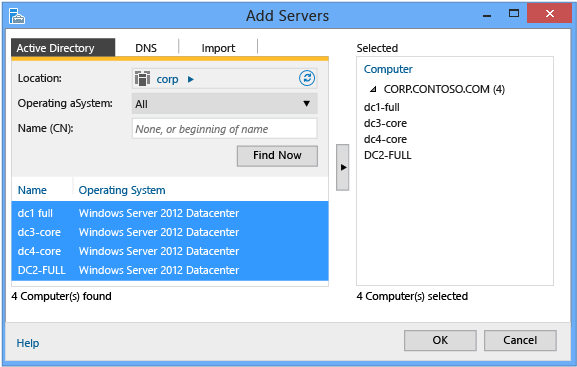
This gives you three ways to add together servers to the pool for use or group:
-
Active Directory search (uses LDAP, requires that the computers belong to a domain, allows operating organization filtering and supports wildcards)
-
DNS search (uses DNS allonym or IP address via ARP or NetBIOS broadcast or WINS lookup, does not allow operating organization filtering or back up wildcards)
-
Import (uses a text file list of servers separated by CR/LF)
Click Discover Now to return a list of servers from that aforementioned Active Directory domain that the computer is joined to, Click one or more than server names from the list of servers. Click the right arrow to add together the servers to the Selected listing. Employ the Add Servers dialog to add selected servers to dashboard role groups. Or Click Manage, and then click Create Server Group, or click Create Server Group on the dashboard Welcome to Server Manager tile to create custom server groups.
Note
The Add Servers procedure does non validate that a server is online or accessible. However, any unreachable servers flag in the Manageability view in Server Manager at the next refresh
You can install roles remotely on any Windows Server 2012 computers added the puddle, as shown:
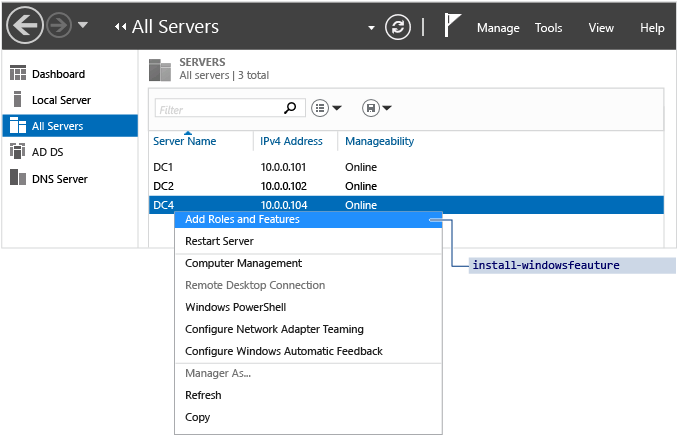
You cannot fully manage servers running operating systems older than Windows Server 2012. The Add Roles and Features selection is running ServerManager Windows PowerShell Module Install-WindowsFeature.
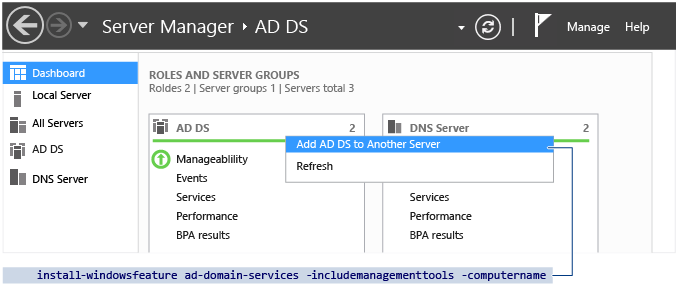
You can also use the Server Managing director Dashboard on an existing domain controller to select remote server Advert DS installation with the office already preselected by correct clicking the Ad DS dashboard tile and selecting Add AD DS to Some other Server. This is invoking Install-WindowsFeature Advertisement-Domain-Services.
The estimator you lot are running Server Managing director on pools itself automatically. To install the AD DS role here, merely click the Manage menu and click Add Roles and Features.
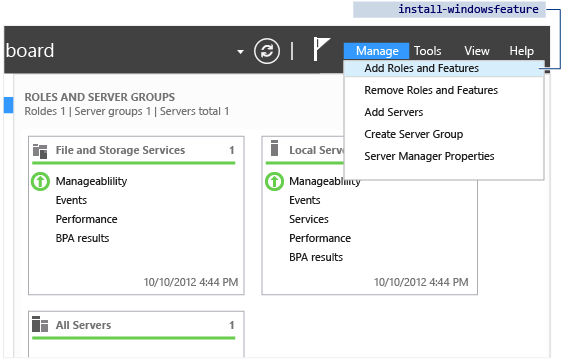
Installation Type
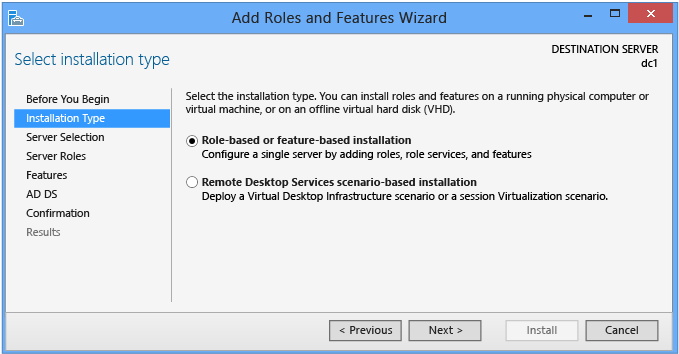
The Installation Type dialog provides an selection that does not support Active Directory Domain Services: the Remote Desktop Services scenario based-installation. That option only allows Remote Desktop Service in a multi-server distributed workload. If you select information technology, AD DS cannot install.
Always go out the default selection in identify when installing Advertizement DS: Office-based or Feature-based Installation.
Server Selection
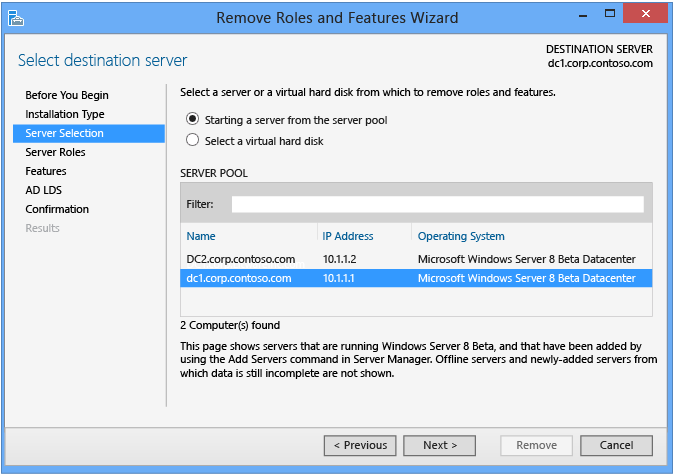
The Server Selection dialog enables you to choose from ane of the servers previously added to the pool, every bit long every bit it is accessible. The local server running Server Director is automatically available.
In addition, you can select offline Hyper-Five VHD files with the Windows Server 2012 operating system and Server Director adds the part to them directly through component servicing. This allows yous to provision virtual servers with the necessary components before further configuring them.
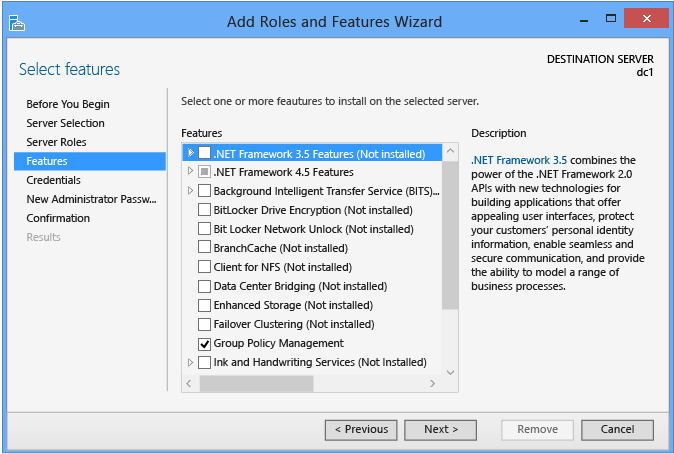
Server Roles and Features
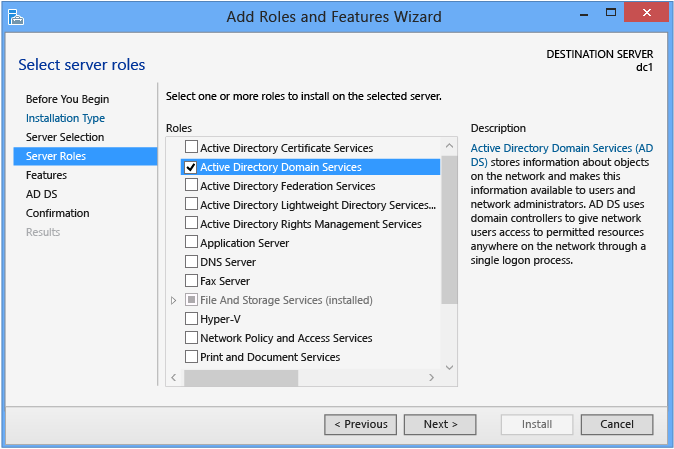
Select the Active Directory Domain Services office if you lot intend to promote a domain controller. All Active Directory administration features and required services install automatically, fifty-fifty if they are ostensibly role of another office or do non appear selected in the Server Director interface.
Server Manager also presents an informational dialog that shows which management features this role implicitly installs; this is equivalent to the -IncludeManagementTools statement.
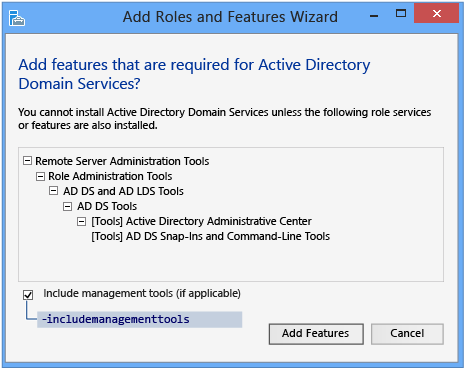
Additional Features tin can be added here as desired.
Active Directory Domain Services
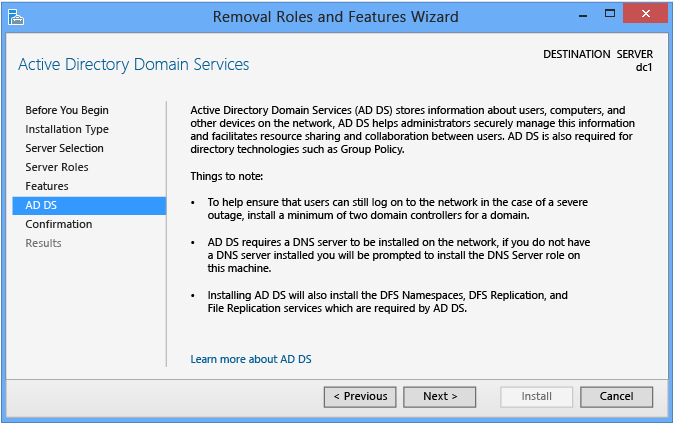
The Active Directory Domain Services dialog provides express data on requirements and all-time practices. It mainly acts every bit a confirmation that you chose the Ad DS role " if this screen does not appear, you did not select AD DS.
Confirmation
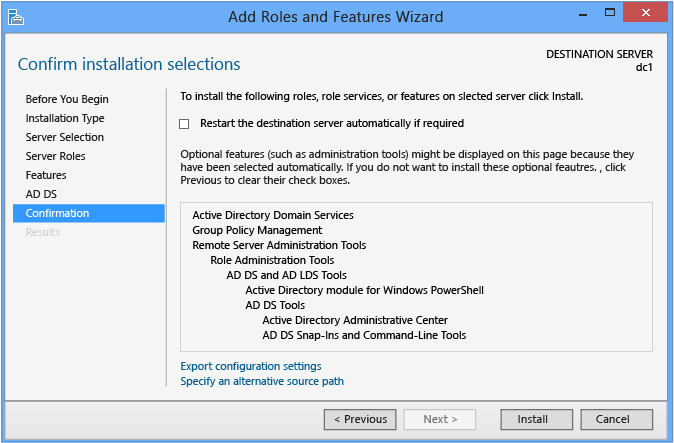
The Confirmation dialog is the final checkpoint before part installation starts. It offers an option to restart the reckoner every bit needed subsequently role installation, merely Advertising DS installation does not require a reboot.
By clicking Install, you confirm you are set to begin role installation. You cannot cancel a function installation once it begins.
Results
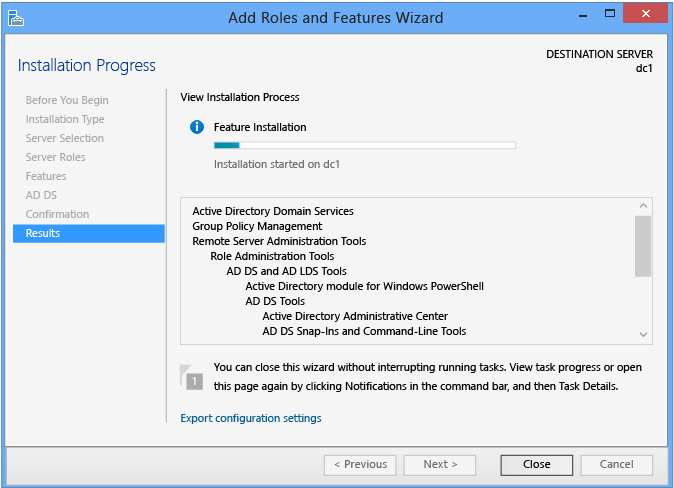
The Results dialog shows the current installation progress and electric current installation condition. Part installation continues regardless of whether Server Manager is airtight.
Verifying the installation results is however a best practice. If yous close the Results dialog before installation completes, you tin check the results using the Server Manager notification flag. Server Director likewise shows a alert message for whatsoever servers that accept installed the AD DS role simply not been farther configured as domain controllers.
Chore Notifications
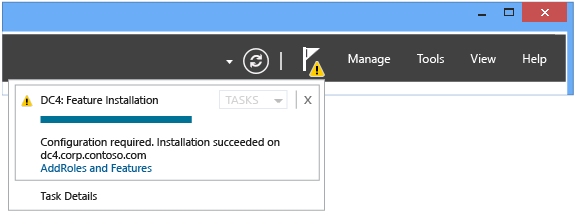
AD DS Details
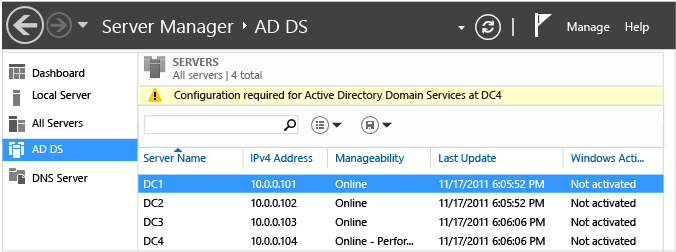
Job Details
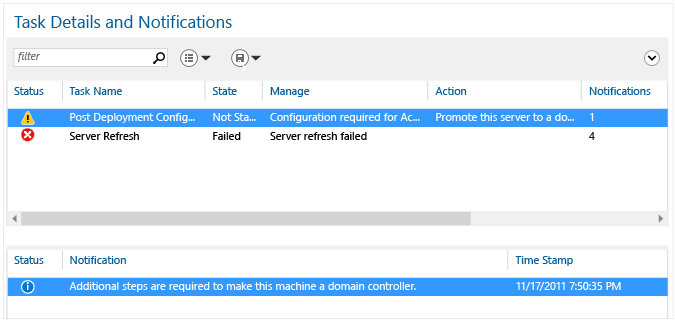
Promote to Domain Controller
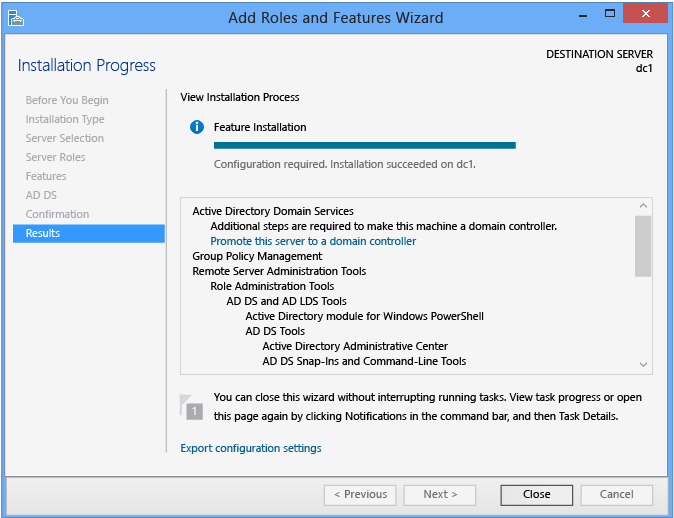
At the end of the AD DS function installation, you can keep with configuration by using the Promote this server to a domain controller link. This is required to make the server a domain controller, simply is not necessary to run the configuration wizard immediately. For example, you may only desire to provision servers with the Advertising DS binaries earlier sending them to another branch function for later configuration. Past adding the Advert DS function before shipping, you save fourth dimension when information technology reaches its destination. You also follow the best practice of not keeping a domain controller offline for days or weeks. Finally, this enables you to update components before domain controller promotion, saving you at least one subsequent reboot.
Selecting this link later invokes the ADDSDeployment cmdlets: install-addsforest, install-addsdomain, or install-addsdomaincontroller.
Uninstalling/Disabling
You remove the AD DS function similar any other role, regardless of whether y'all promoted the server to a domain controller. However, removing the Advertisement DS role requires a restart on completion.
Active Directory Domain Services role removal is unlike from installation, in that it requires domain controller demotion before it can consummate. This is necessary to forestall a domain controller from having its part binaries uninstalled without proper metadata cleanup in the wood. For more information, see Demoting Domain Controllers and Domains (Level 200).
Alert
Removing the AD DS roles with Dism.exe or the Windows PowerShell DISM module after promotion to a Domain Controller is not supported and will prevent the server from booting normally.
Different Server Manager or the AD DS Deployment module for Windows PowerShell, DISM is a native servicing arrangement that has no inherent knowledge of Advertizement DS or its configuration. Exercise not utilise Dism.exe or the Windows PowerShell DISM module to uninstall the AD DS role unless the server is no longer a domain controller.
Create an AD DS Forest Root Domain with Server Managing director
The following diagram illustrates the Active Directory Domain Services configuration process, in the case where y'all accept previously installed the AD DS function and started the Agile Directory Domain Services Configuration Wizard using Server Managing director.
Deployment Configuration
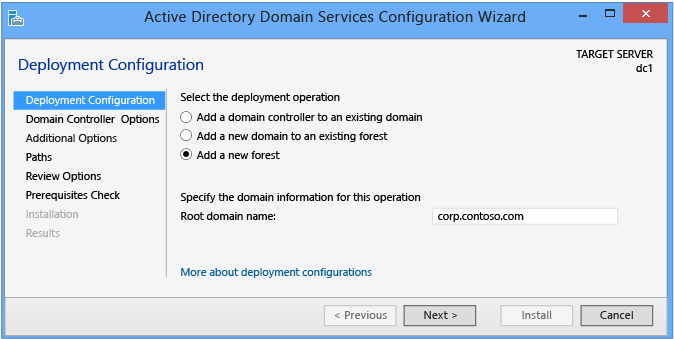
Server Managing director begins every domain controller promotion with the Deployment Configuration folio. The remaining options and required fields change on this page and subsequent pages, depending on which deployment operation you select.
To create a new Active Directory forest, click Add together a new forest. Yous must provide a valid root domain name; the proper name cannot be single-labeled (for example, the name must be contoso.com or similar and not merely contoso) and must use allowed DNS domain naming requirements.
For more than information on valid domain names, see KB article Naming conventions in Active Directory for computers, domains, sites, and OUs.
Warning
Practice not create new Agile Directory forests with the same name as an external DNS proper noun. For example, if your Internet DNS URL is http://contoso.com, yous must cull a dissimilar proper name for your internal forest to avoid future compatibility issues. That proper noun should be unique and unlikely for web traffic. For example: corp.contoso.com.
A new forest does not need new credentials for the domain'southward Administrator account. The domain controller promotion procedure uses the credentials of the built-in Administrator account from the first domain controller used to create the wood root. There is no style (by default) to disable or lock out the built-in Ambassador account and information technology may be the just entry point into a forest if the other administrative domain accounts are unusable. It is critical to know the password earlier deploying a new woods.
DomainName requires a valid fully qualified domain DNS name and is required.
Domain Controller Options
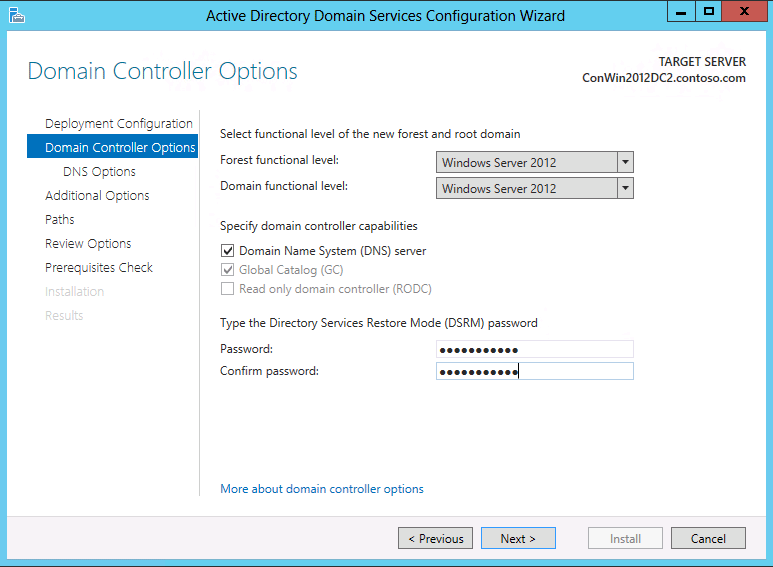
The Domain Controller Options enables you to configure the woods functional level and domain functional level for the new wood root domain. Past default, these settings are Windows Server 2012 in a new wood root domain. The Windows Server 2012 forest functional level does not provide any new functionality over the Windows Server 2008 R2 wood functional level. The Windows Server 2012 domain functional level is required merely in gild to implement the new Kerberos settings "e'er provide claims" and "Fail unarmored authentication requests." A primary utilize for functional levels in Windows Server 2012 is to restrict participation in the domain to domain controllers that meet minimum-allowed operating system requirements. In other words, you can specify Windows Server 2012 domain functional level merely domain controllers that run Windows Server 2012 can host the domain. Windows Server 2012 implements a new domain controller flag called DS_WIN8_REQUIRED in the DSGetDcName role of NetLogon that exclusively locates Windows Server 2012 domain controllers. This allows you the flexibility of a more homogeneous or heterogeneous forest in terms of which operating systems are permitted to be run on domain controllers.
For more than information nigh domain controller Location, review Directory Service Functions.
The only configurable domain controller capability is the DNS server option. Microsoft recommends that all domain controllers provide DNS services for high availability in distributed environments, which is why this choice is selected by default when installing a domain controller in any mode or domain. The Global Itemize and read just domain controller options are unavailable when creating a new wood root domain; the beginning domain controller must exist a GC, and cannot be a read simply domain controller (RODC).
The specified Directory Services Restore Mode Countersign must attach to the password policy applied to the server, which past default does not crave a strong password; but a non-blank i. Always cull a strong, complex password or preferably, a passphrase.
DNS Options and DNS Delegation Credentials
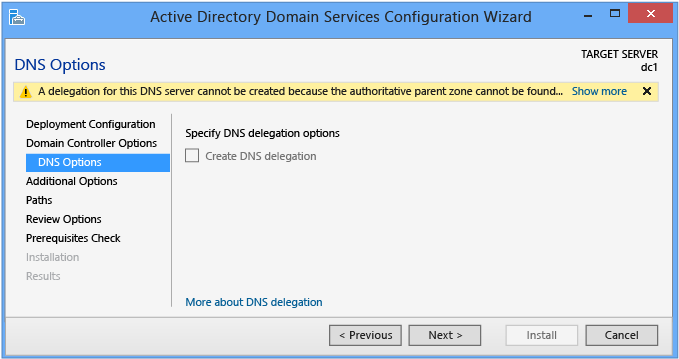
The DNS Options page enables you to configure DNS delegation and provide alternate DNS administrative credentials.
Yous cannot configure DNS options or delegation in the Agile Directory Domain Services Configuration Wizard when installing a new Active Directory Woods Root Domain where you selected the DNS server on the Domain Controller Options folio. The Create DNS delegation option is available when creating a new forest root DNS zone in an existing DNS server infrastructure. This option enables you to provide alternate DNS authoritative credentials that have the rights to update DNS zone.
For more information most whether you lot need to create a DNS delegation, see Agreement Zone Delegation.
Boosted Options

The Additional Options folio shows the NetBIOS proper noun of the domain and enables you to override it. By default, the NetBIOS domain proper noun matches the left-about label of the fully qualified domain proper noun provided on the Deployment Configuration page. For example, if you provided the fully qualified domain name of corp.contoso.com, the default NetBIOS domain name is CORP.
If the name is 15 characters or less and does non conflict with some other NetBIOS name, it is unaltered. If it does conflict with another NetBIOS name, a number is appended to the name. If the proper noun is more than 15 characters, the wizard provides a unique, truncated suggestion. In either case, the wizard offset validates the name is not already in use via a WINS lookup and NetBIOS circulate.
For more information on valid domain names, see KB article Naming conventions in Agile Directory for computers, domains, sites, and OUs.
Paths
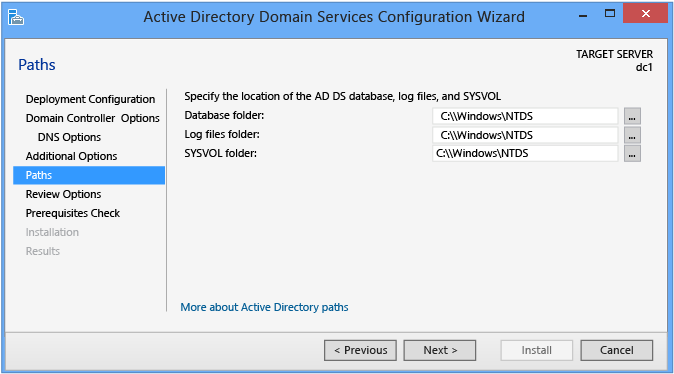
The Paths page enables you to override the default folder locations of the Advertizing DS database, the database transaction logs, and the SYSVOL share. The default locations are always in subdirectories of %systemroot% (i.e. C:\Windows).
Review Options and View Script
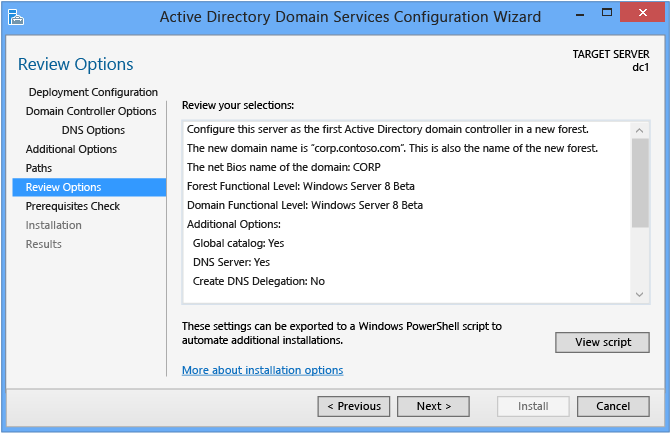
The Review Options page enables you to validate your settings and ensure they run across your requirements earlier you kickoff the installation. This is non the last opportunity to stop the installation when using Server Manager. This is simply an option to ostend your settings earlier standing the configuration
The Review Options page in Server Director also offers an optional View Script button to create a Unicode text file that contains the current ADDSDeployment configuration every bit a single Windows PowerShell script. This enables yous to use the Server Manager graphical interface as a Windows PowerShell deployment studio. Use the Active Directory Domain Services Configuration Wizard to configure options, consign the configuration, and then cancel the magician. This procedure creates a valid and syntactically correct sample for further modification or direct use. For example:
# # Windows PowerShell Script for AD DS Deployment # Import-Module ADDSDeployment Install-ADDSForest ` -CreateDNSDelegation ` -DatabasePath "C:\Windows\NTDS" ` -DomainMode "Win2012" ` -DomainName "corp.contoso.com" ` -DomainNetBIOSName "CORP" ` -ForestMode "Win2012" ` -InstallDNS:$truthful ` -LogPath "C:\Windows\NTDS" ` -NoRebootOnCompletion:$faux ` -SYSVOLPath "C:\Windows\SYSVOL" -Strength:$true Note
Server Director generally fills in all arguments with values when promoting and does not rely on defaults (as they may modify between time to come versions of Windows or service packs). The one exception to this is the -safemodeadministratorpassword argument (which is deliberately omitted from the script). To force a confirmation prompt, omit the value when running cmdlet interactively.
Prerequisites Check
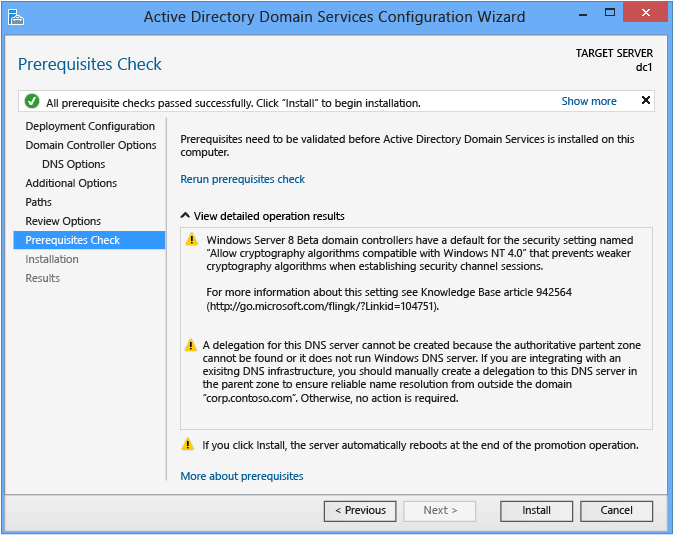
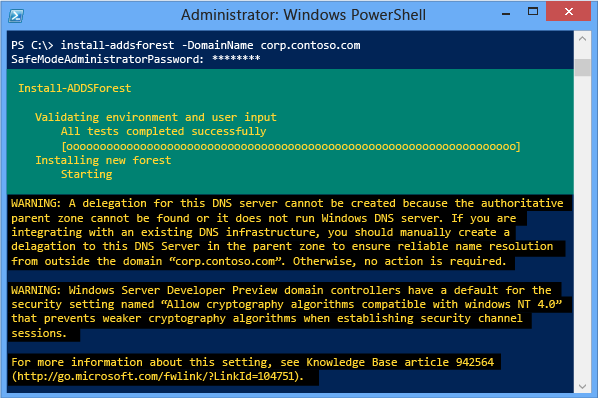
The Prerequisites Check is a new feature in AD DS domain configuration. This new phase validates that the server configuration is capable of supporting a new Advert DS forest.
When installing a new woods root domain, the Server Manager Active Directory Domain Services Configuration Wizard invokes a serial of modular tests. These tests alert yous with suggested repair options. You can run the tests as many times as required. The domain controller process cannot keep until all prerequisite tests pass.
The Prerequisites Check likewise surfaces relevant information such as security changes that bear upon older operating systems.
For more information on the specific prerequisite checks, run into Prerequisite Checking.
Installation
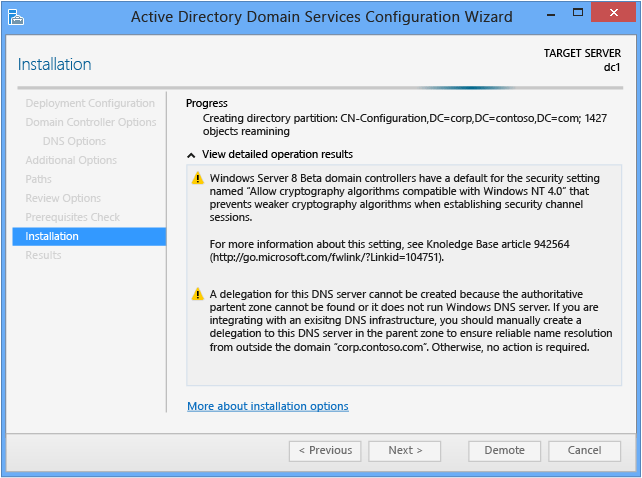
When the Installation folio displays, the domain controller configuration begins and cannot be halted or canceled. Detailed operations display on this page and are written to logs:
-
%systemroot%\debug\dcpromo.log
-
%systemroot%\debug\dcpromoui.log
Annotation
You can run multiple office installation and Advertizing DS configuration wizards from the aforementioned Server Director console simultaneously.
Results
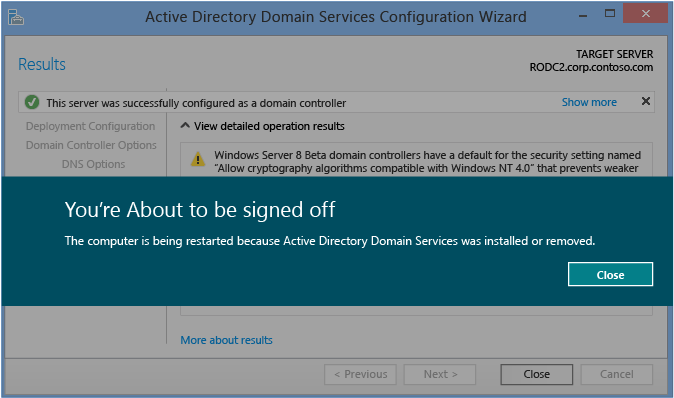
The Results page shows the success or failure of the promotion and any important authoritative data. The domain controller will automatically reboot after ten seconds.
Deploying a Forest with Windows PowerShell
This department explains how to install the first domain controller in a wood root domain using Windows PowerShell on a Core Windows Server 2012 computer.
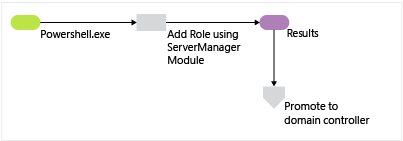
Windows PowerShell AD DS Role Installation Process
By implementing a few straightforward ServerManager deployment cmdlets into your deployment processes, you farther realize the vision of AD DS simplified administration.
The side by side figure illustrates the Active Directory Domain Services role installation process, commencement with yous running PowerShell.exe and ending right before the promotion of the domain controller.
| ServerManager Cmdlet | Arguments (Bold arguments are required. Italicized arguments tin be specified by using Windows PowerShell or the Advertizing DS Configuration Wizard.) |
|---|---|
| Install-WindowsFeature/Add-WindowsFeature | -Proper name -Restart -IncludeAllSubFeature -IncludeManagementTools -Source -ComputerName -Credential -LogPath -Vhd -ConfigurationFilePath |
Notation
While not required, the statement -IncludeManagementTools is highly recommended when installing the Ad DS part binaries
The ServerManager module exposes office installation, status, and removal portions of the new DISM module for Windows PowerShell. This layering simplifies the most tasks and reduces need for direct usage of the powerful (but dangerous when misused) DISM module.
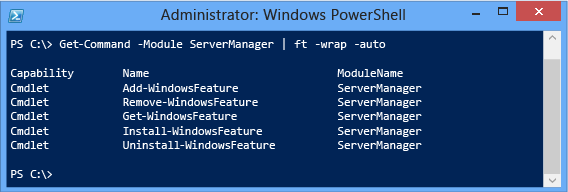
Use Get-Command to export the aliases and cmdlets in ServerManager.
Become-Command -module ServerManager For example:
To add the Active Directory Domain Services function, simply run the Install-WindowsFeature with the Advertizing DS role name as an argument. Like Server Managing director, all required services implicit to the AD DS role install automatically.
Install-WindowsFeature -proper noun AD-Domain-Services If you also want the AD DS direction tools installed - and this is highly recommended - then provide the -IncludeManagementTools argument:
Install-WindowsFeature -proper noun Advertizing-Domain-Services -IncludeManagementTools For instance:
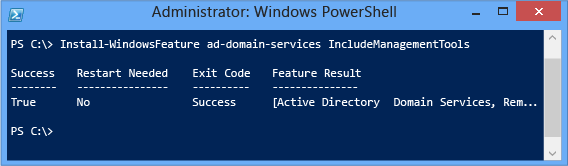
To list all features and roles with their installation status, employ Get-WindowsFeature without arguments. Specify -ComputerName argument for the installation status from a remote server.
Get-WindowsFeature Because Get-WindowsFeature does not have a filtering machinery, y'all must use Where-Object with a pipeline to find specific features. The pipeline is a channel used betwixt multiple cmdlets to pass data and the Where-Object cmdlet acts as a filter. The built-in $_ variable acts as the current object passing through the pipeline with whatsoever properties it may incorporate.
Go-WindowsFeature | where-object <options> For example, to find all features containing "Agile Dir" in their Display Proper noun belongings, utilise:
Get-WindowsFeature | where displayname -like "*agile dir*" Further examples illustrated beneath:
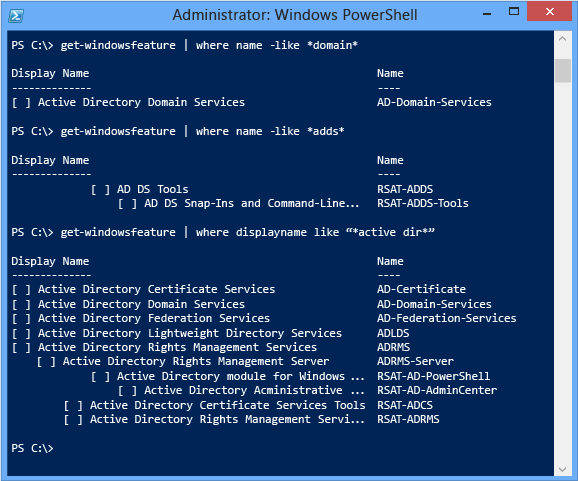
For more information almost more Windows PowerShell operations with pipelines and Where-Object, see Piping and the Pipeline in Windows PowerShell.
Note as well that Windows PowerShell 3.0 significantly simplified the control-line arguments needed in this pipeline performance. Windows PowerShell two.0 would have required:
Get-WindowsFeature | where {$_.displayname - like "*active dir*"} By using the Windows PowerShell pipeline, y'all can create readable results. For example:
Install-WindowsFeature | Format-Listing Install-WindowsFeature | select-object | Format-List 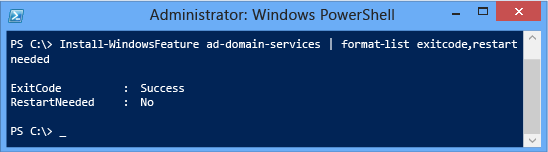
Note how using the Select-Object cmdlet with the -expandproperty argument returns interesting data:
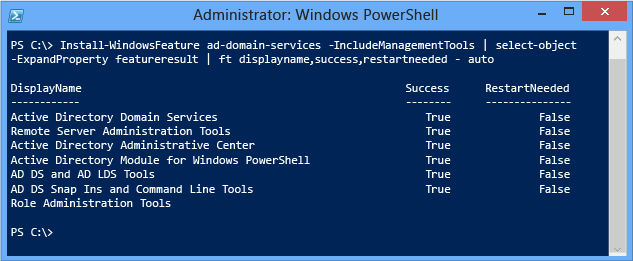
Note
The Select-Object -expandproperty statement slows down overall installation functioning slightly.
Create an AD DS Forest Root Domain with Windows PowerShell
To install a new Active Directory woods using the ADDSDeployment module, use the following cmdlet:
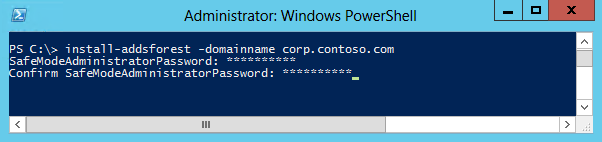
Install-addsforest The Install-AddsForest cmdlet only has two phases (prerequisite checking and installation). The two figures below show the installation stage with the minimum required statement of -domainname.
| ADDSDeployment Cmdlet | Arguments (Bold arguments are required. Italicized arguments tin can be specified past using Windows PowerShell or the AD DS Configuration Wizard.) |
|---|---|
| Install-Addsforest | -Confirm -CreateDNSDelegation -DatabasePath -DomainMode -DomainName -DomainNetBIOSName -DNSDelegationCredential -ForestMode -Forcefulness -InstallDNS -LogPath -NoDnsOnNetwork -NoRebootOnCompletion -SafeModeAdministratorPassword -SkipAutoConfigureDNS -SkipPreChecks -SYSVOLPath -Whatif |
Note
The -DomainNetBIOSName argument is required if you want to change the automatically generated 15-graphic symbol name based on the DNS domain name prefix or if the proper noun exceeds fifteen characters.
The equivalent Server Manager Deployment Configuration ADDSDeployment cmdlet and arguments are:
Install-ADDSForest -DomainName <string> The equivalent Server Managing director Domain Controller Options ADDSDeployment cmdlet arguments are:
-ForestMode <{Win2003 | Win2008 | Win2008R2 | Win2012 | Default}> -DomainMode <{Win2003 | Win2008 | Win2008R2 | Win2012 | Default}> -InstallDNS <{$false | $true}> -SafeModeAdministratorPassword <secure cord> The Install-ADDSForest arguments follow the same defaults as Server Manager if not specified.
The SafeModeAdministratorPassword argument'due south operation is special:
-
If not specified as an statement, the cmdlet prompts you to enter and confirm a masked password. This is the preferred usage when running the cmdlet interactively.
For example, to create a new forest named corp.contoso.com and be prompted to enter and ostend a masked password:
Install-ADDSForest "DomainName corp.contoso.com -
If specified with a value, the value must exist a secure string. This is not the preferred usage when running the cmdlet interactively.
For example, you tin can manually prompt for a password by using the Read-Host cmdlet to prompt the user for a secure cord:
-safemodeadministratorpassword (read-host -prompt "Password:" -assecurestring) Warning
Equally the previous choice does not ostend the password, apply farthermost caution: the password is not visible.
You can also provide a secure cord as a converted clear-text variable, although this is highly discouraged.
-safemodeadministratorpassword (convertto-securestring "Password1" -asplaintext -strength) Finally, you could shop the obfuscated password in a file, and and so reuse information technology later, without the clear text password e'er actualization. For instance:
$file = "c:\prisoner of war.txt" $prisoner of war = read-host -prompt "Password:" -assecurestring $pw | ConvertFrom-SecureString | Set-Content $file -safemodeadministratorpassword (Get-Content $File | ConvertTo-SecureString) Warning
Providing or storing a articulate or obfuscated text password is not recommended. Anyone running this command in a script or looking over your shoulder knows the DSRM countersign of that domain controller. Anyone with access to the file could reverse that obfuscated password. With that knowledge, they can logon to a DC started in DSRM and eventually impersonate the domain controller itself, elevating their privileges to the highest level in an Active Directory woods. An boosted set of steps using System.Security.Cryptography to encrypt the text file data is advisable but out of scope. The all-time practice is to totally avoid countersign storage.
The ADDSDeployment cmdlet offers an additional pick to skip automated configuration of DNS customer settings, forwarders, and root hints. You cannot skip this configuration pick when using Server Manager. This argument matters only if you lot installed the DNS Server role prior to configuring the domain controller:
-SkipAutoConfigureDNS The DomainNetBIOSName operation is also special:
-
If the DomainNetBIOSName argument is not specified with a NetBIOS domain name and the unmarried-label prefix domain proper name in the DomainName statement is xv characters or fewer, then promotion continues with an automatically generated name.
-
If the DomainNetBIOSName statement is not specified with a NetBIOS domain proper name and the unmarried-label prefix domain name in the DomainName statement is xvi characters or more, then promotion fails.
-
If the DomainNetBIOSName argument is specified with a NetBIOS domain name of 15 characters or fewer, then promotion continues with that specified proper name.
-
If the DomainNetBIOSName argument is specified with a NetBIOS domain name of 16 characters or more than, then promotion fails.
The equivalent Server Manager Additional Options ADDSDeployment cmdlet statement is:
-domainnetbiosname <string> The equivalent Server Managing director Paths ADDSDeployment cmdlet arguments are:
-databasepath <string> -logpath <string> -sysvolpath <string> Use the optional Whatif argument with the Install-ADDSForest cmdlet to review configuration information. This enables you to see the explicit and implicit values of a cmdlet's arguments.
For instance:
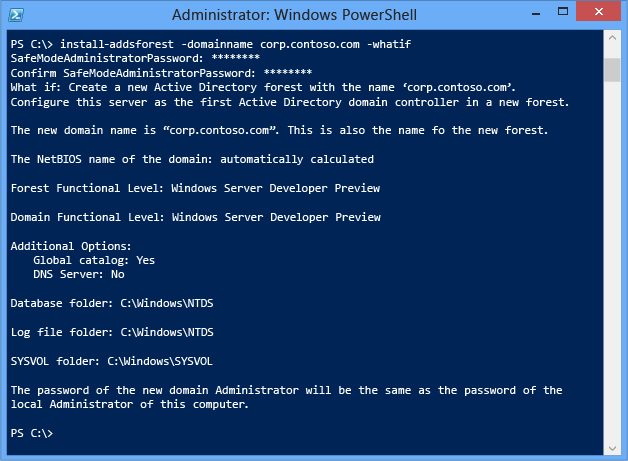
You cannot bypass the Prerequisite Cheque when using Server Managing director, but you lot can skip the process when using the AD DS Deployment cmdlet using the following statement:
-skipprechecks Alarm
Microsoft discourages skipping the prerequisite cheque as it tin lead to a partial domain controller promotion or damaged Advertisement DS woods.
Note how, just like Server Manager, Install-ADDSForest reminds yous that promotion volition reboot the server automatically.
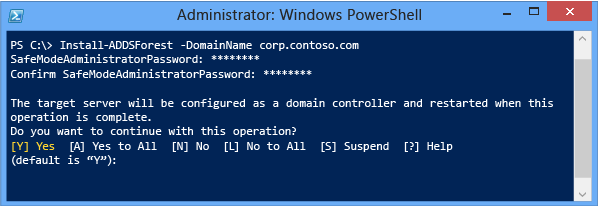
To take the reboot prompt automatically, use the -strength or -confirm:$false arguments with any ADDSDeployment Windows PowerShell cmdlet. To prevent the server from automatically rebooting at the terminate of promotion, utilize the -norebootoncompletion argument.
Warning
Overriding the reboot is discouraged. The domain controller must reboot to function correctly.
Come across Likewise
Active Directory Domain Services (TechNet Portal) Active Directory Domain Services for Windows Server 2008 R2 Active Directory Domain Services for Windows Server 2008 Windows Server Technical Reference (Windows Server 2003) Active Directory Authoritative Center: Getting Started (Windows Server 2008 R2) Agile Directory Administration with Windows PowerShell (Windows Server 2008 R2) Enquire the Directory Services Team (Official Microsoft Commercial Technical Back up Blog)
Feedback
Submit and view feedback for
Source: https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/windows-server/identity/ad-ds/deploy/install-a-new-windows-server-2012-active-directory-forest--level-200-
Posted by: kleinsenjoyergoo.blogspot.com

0 Response to "How To Add A New Forest In Windows Server 2016"
Post a Comment